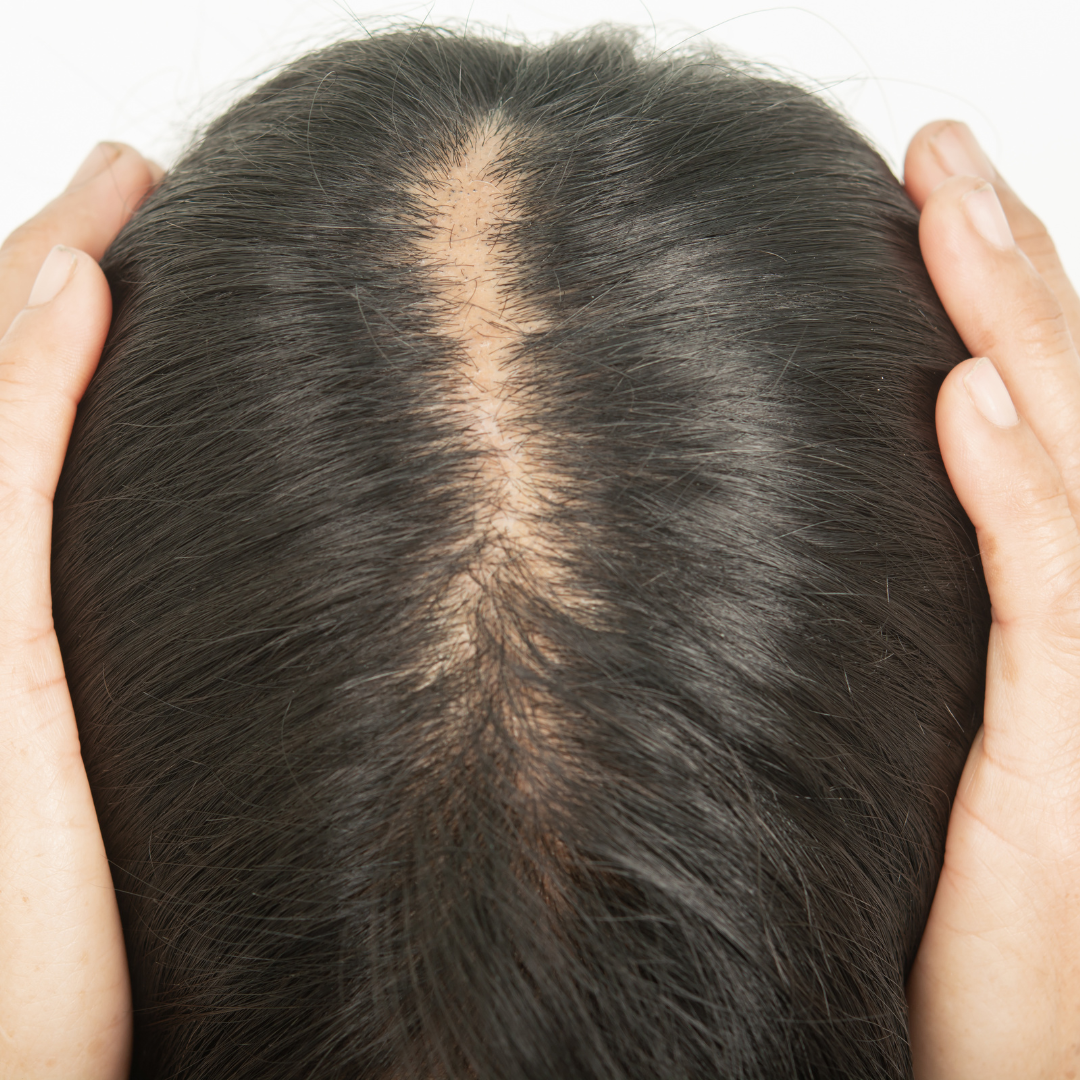
Understanding Hair Miniaturization
Hair miniaturization is a term often used in discussions about hair loss and its progression. It refers to the gradual miniaturization of hair follicles, leading to finer, shorter, and overall more miniaturized hair and hair growth over time and . Understanding this phenomenon is crucial for addressing hair loss effectively. In this article, we’ll delve into the causes, effects, and potential solutions for hair miniaturization.
Hair Miniaturization: How To Tell
Identifying hair follicle miniaturization is a critical first step in the process of addressing the issue. The following symptoms to look out for:
Thinning hair:
Hair strands become progressively finer and weaker, resulting in a visibly thinner appearance.
Receding hairline:
In men, miniaturization often begins at the temples and crown, leading to a receding hairline and eventual balding.
Sparse scalp coverage:
As hair follicles shrink, they produce fewer and thinner strands, leading to patches of scalp becoming visible.
Decreased hair density:
Hair miniaturization can reduce the overall density of hair on the scalp, making it appear sparse and less voluminous. This decreased hair density is even more pronounced when analyzing through a microscope.
Hair Miniaturization and Telogen Effluvium
Hair miniaturization and telogen effluvium are both hair loss conditions but with distinct causes and characteristics. Hair miniaturization, or follicle miniaturization, involves the gradual shrinking of hair follicles, resulting in finer, weaker, and just generally speaking miniaturized hairs and poor hair growth over time, often associated with genetic predispositions and hormonal imbalances. On the other hand, telogen effluvium is a temporary form of hair loss triggered by factors such as stress, illness, or hormonal changes, leading to a sudden shedding of hair in the telogen (resting) phase of the hair growth cycle. While both conditions can result in thinning hair, understanding their differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
A Point About Female Hair Miniaturization
Female hair miniaturization, similar to its male counterpart, involves the gradual shrinking of hair follicles, leading to finer, weaker hair growth. While it can result from genetic factors and hormonal imbalances like androgenetic alopecia, it’s often less predictable in women. Female hair miniaturization typically manifests as diffuse thinning across the scalp rather than specific patterns of baldness. Hormonal fluctuations due to pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders can exacerbate the difference between miniaturized hair vs normal hair. Addressing underlying causes and utilizing treatments such as medications, nutritional supplements, and low-level laser therapy can help women combat hair miniaturization and maintain healthy hair density. So if you’re wondering, “what does hair miniaturization look like in women?” the signs are very similar to those of women.
Causes of Hair Miniaturization: Understanding follicular miniaturization
Hair miniaturization or miniaturized hair follicles can result from various factors, both genetic and environmental. One primary cause is genetics, particularly the presence of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) sensitivity in hair follicles. DHT is a hormone derived from testosterone, and in individuals with a genetic predisposition, it can bind to hair follicles, causing them to shrink over time and leading to miniaturizing hair. This process gradually shortens the hair growth cycle and produces thinner, weaker and continually shrinking hair follicles.
What causes hair follicles to shrink?:
Age:
As individuals age, hormonal changes can affect hair follicle function, leading to miniaturization.
Hormonal imbalances:
Fluctuations in hormone levels, such as those experienced during pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid disorders, can contribute to hair miniaturization.
Poor nutrition:
Inadequate intake of essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and proteins can weaken hair follicles and contribute to miniaturization.
Stress:
Chronic stress can disrupt hormone levels and blood circulation to the scalp, exacerbating hair loss and miniaturization.
Environmental factors:
Exposure to pollutants, UV radiation, and harsh chemicals in hair care products can damage hair follicles, leading to miniaturization.
Can miniaturized hair grow back?
Miniaturized hair can potentially grow back, depending on the cause and extent of damage. Temporary factors like stress or medication side effects may allow for regrowth once the underlying issue resolves. However, in cases of genetic hair loss, such as androgenetic alopecia, follicle damage may be permanent, making regrowth more challenging.
Solutions for Hair Miniaturization: How to stop hair miniaturization
While hair miniaturization can be a challenging issue to address, several solutions can help manage and potentially reverse its effects. These include:
Medications:
FDA-approved medications such as minoxidil and finasteride can help slow down hair miniaturization and promote hair regrowth by inhibiting the effects of DHT on hair follicles.
Nutritional supplements:
Supplements containing essential vitamins, minerals, and amino acids, such as biotin, zinc, and iron, can support hair health and combat miniaturization.
Laser therapy:
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) devices stimulate blood circulation to the scalp and promote cellular activity in hair follicles, potentially reversing miniaturization and promoting hair regrowth.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy:
PRP therapy involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood into the scalp to stimulate hair follicle regeneration and promote thicker, healthier hair growth.
Hair transplant surgery:
In cases of advanced hair loss, hair transplant surgery can restore hair density by transplanting healthy hair follicles from donor areas to balding or thinning areas of the scalp.
Conclusion:
Hair miniaturization is a common precursor to hair loss, affecting both men and women worldwide. Understanding its causes, effects, and potential solutions is essential for effectively managing this condition. By addressing underlying factors such as genetics, hormonal imbalances, and nutrient deficiencies, individuals learn how to stop hair miniaturization and maintain healthy, vibrant hair. Consulting with a dermatologist or hair loss specialist can provide personalized treatment recommendations tailored to individual needs and preferences, helping individuals regain confidence and achieve optimal hair health.